Jenkins is an open source, Java-based automation server that offers an easy way to set up a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
Continuous Integration (CI) is the process of automating the build and testing of code every time a team member commits changes to version control. Continuous Delivery (CD) is the process to build, test, configure and deploy from a build to a production environment.
This tutorial demonstrates the steps of installing Jenkins on a CentOS 7 system using the official Jenkins repository.
Prerequisites
Before continuing with this tutorial, make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges.
Installing Jenkins
# sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel.x86_64
– Once the installation is completed, you can check the installed version using the following command:
# java -version openjdk version "1.8.0_161" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_161-b14) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.161-b14, mixed mode)
# sudo curl --silent --location http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo [jenkins] name=Jenkins-stable baseurl=http://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable gpgcheck=1
# sudo rpm --import https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
# sudo yum install jenkins
# systemctl enable jenkins # systemctl start jenkins
Adjust the Firewall
Jenkins by default is listening on port 8080, Before accessing the Jenkins server, Use the following commands to open the necessary port:
# sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp # sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Setting Up Jenkins
– Let’s now setup Jenkins, open your browser and type your domain or IP address followed by port 8080:
http://your_ip_or_domain:8080
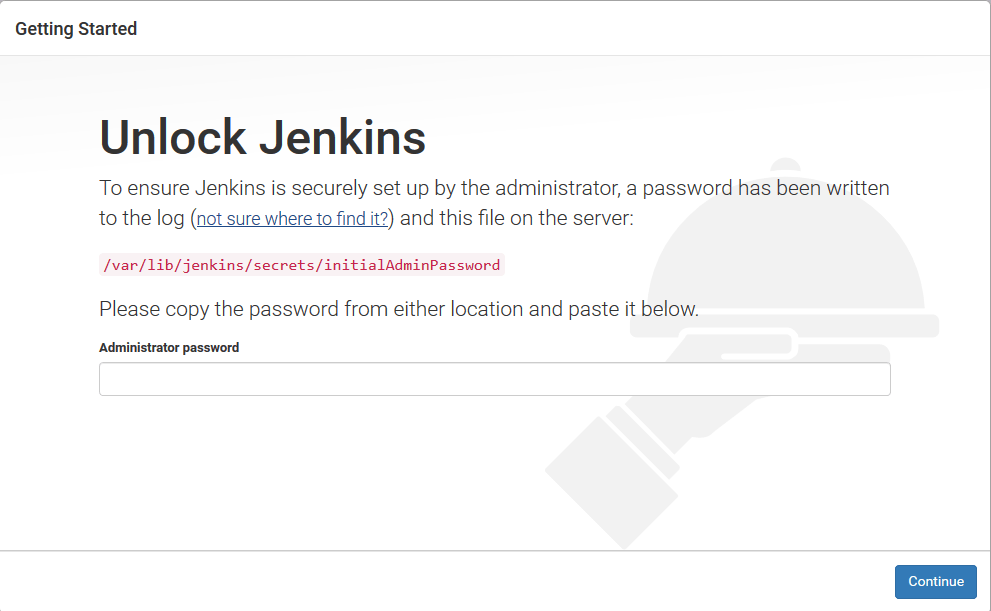
– Copy the password from your terminal, paste it into the Administrator password field and click Continue.
# sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword 5896880025db4b99b80542df52eba7fc
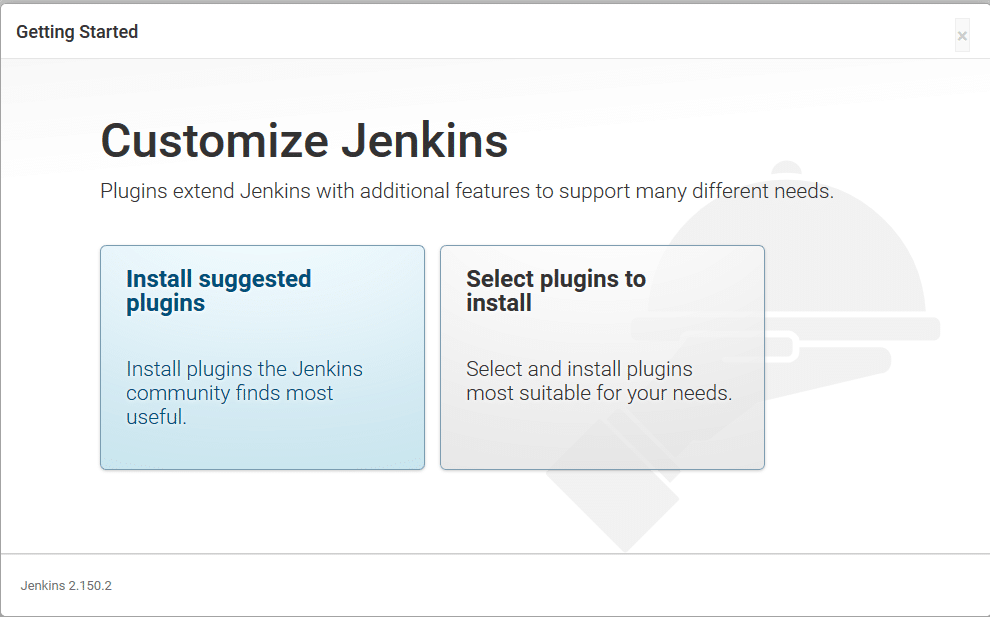
– Click on the Install suggested plugins box, and the installation process will start immediately as below:
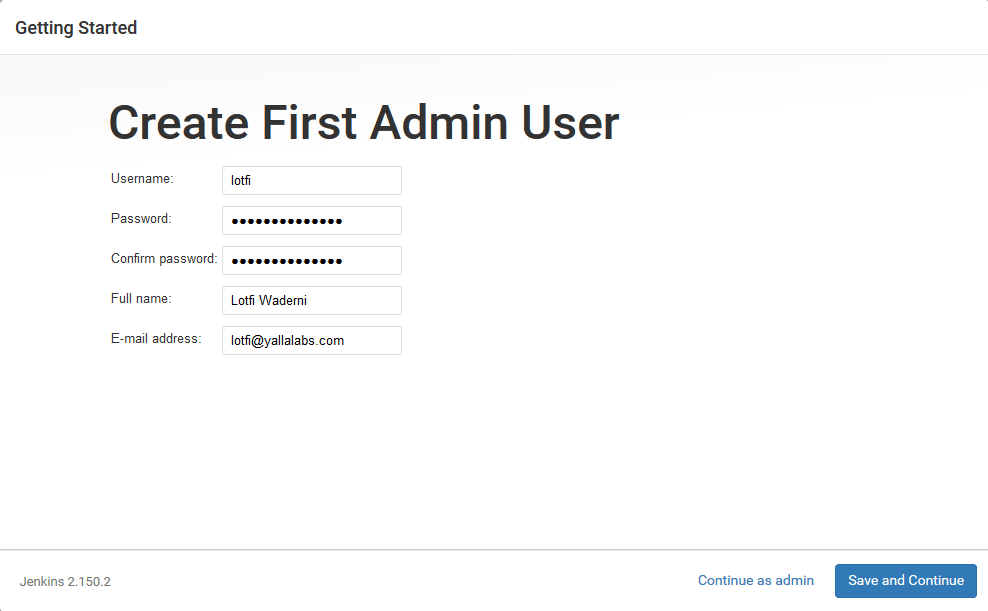
– Once the installation is complete, you will be prompted to set up the first administrative user. Fill out all required information and click Save and Continue.
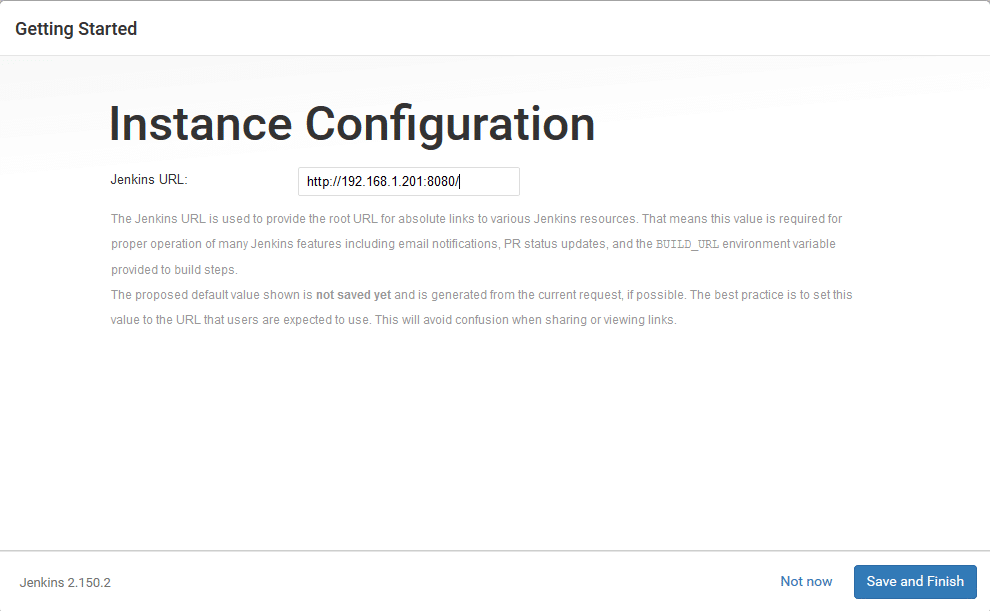
– On the next page you will be asked to set the URL for the Jenkins instance. The URL filed will be populated with an automatically generated URL . To complete the setup confirm the URL by clicking on the Save and Finish button.
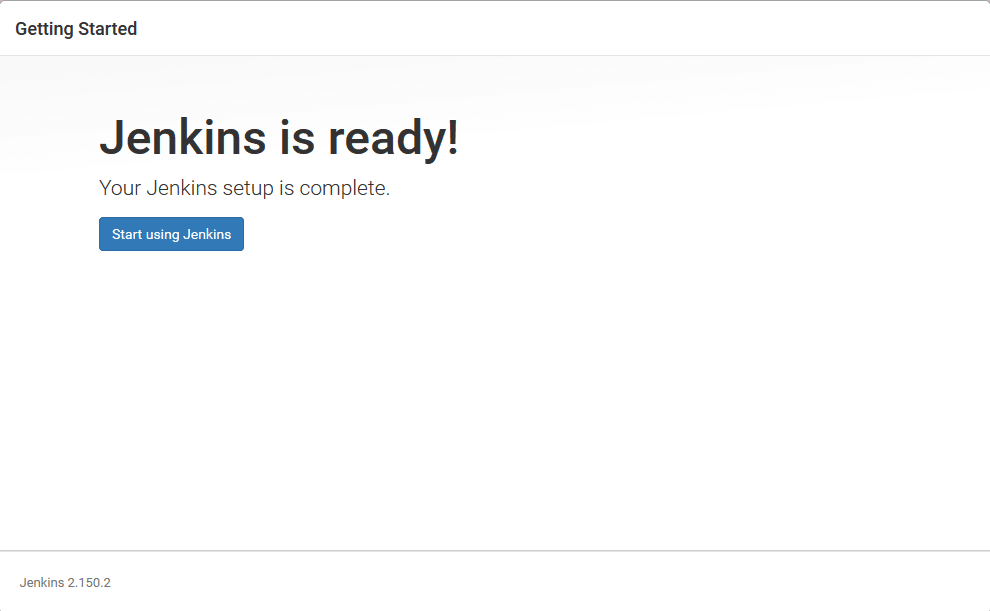
– Finally, click on the Start using Jenkins button and you will be redirected to the Jenkins dashboard logged in as the admin user you have created in one of the previous steps.
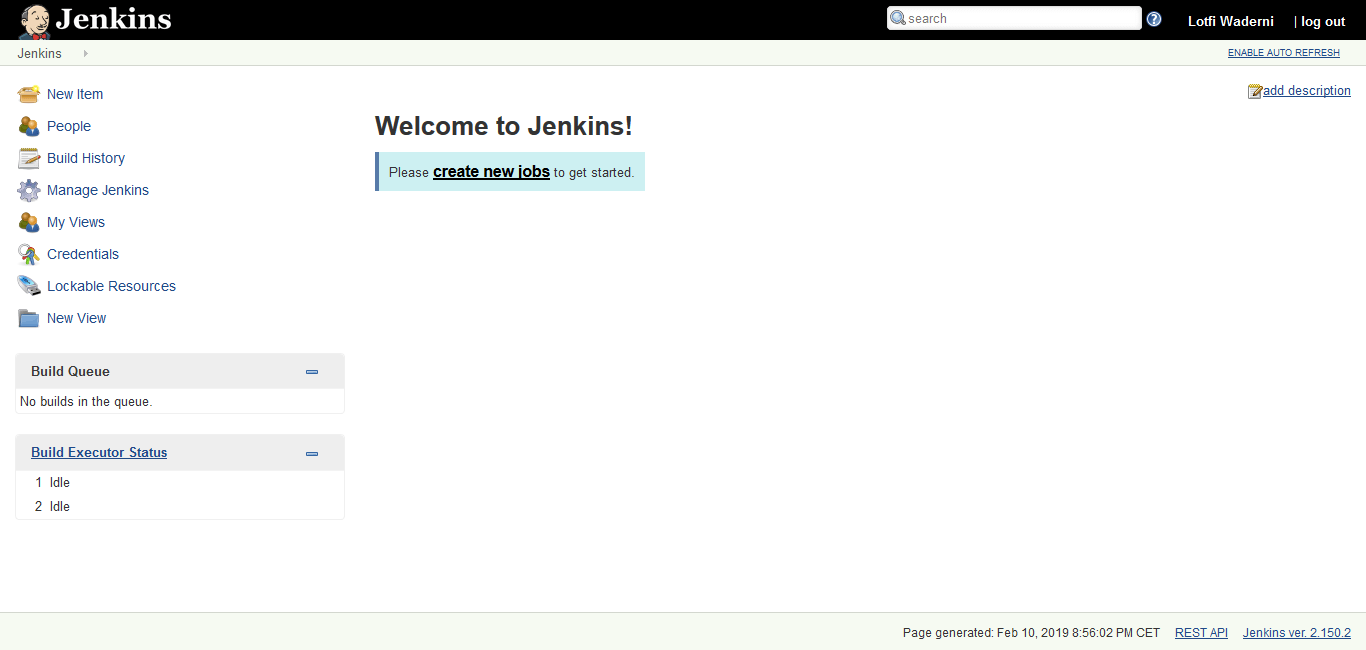
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned how to install and complete the initial configuration of Jenkins on CentOS/RHEL based systems. You might want to check the following guides:
- How to install Apache Maven on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
- How to Install Gradle on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
- Install Latest Version of Git on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
- Add a new Slave Node to Jenkins
We hope this tutorial was enough Helpful. If you need more information, or have any questions, just comment below and we will be glad to assist you!



2 comments
Thank you so much
You are welcome any time