Cockpit is a web-based server management tool for Linux. Although, Cockpit allows you to perform Service Management, User Account Management, SELinux Policy management, Storage Management( NFS Client setup, iSCSI Initiator configurations),…
This guide demonstrates how to install the Cockpit web-based interface on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS / Ubuntu 18.04 LTS to manage your Linux Servers.
Prerequisites
You’ll need to be logged in as a user with sudo privileges in order to install Cockpit
Installing Cockpit on Ubuntu 18.04 / 16.04 LTS
01- Cockpit tool is available in Ubuntu repositories, use the following command to start the installation:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install cockpit
02- Allow external connections to port 9090 through the firewall ufw:
$ sudo ufw allow 9090
03- Enable and start the cockpit.socket service:
$ sudo systemctl start cockpit.socket $ sudo systemctl enable cockpit.socket
Accessing the Cockpit Dashboard web-interface
01- Once you finished with installation. Connect to the Cockpit web interface locally by entering http://localhost:9090 or by entering your IP address http://IP_ADDRESS:9090 to your browser.
02- Log into the Cockpit interface with the same user name and password that you would normally use to log into the system.
Exploring Cockpit Dashboard
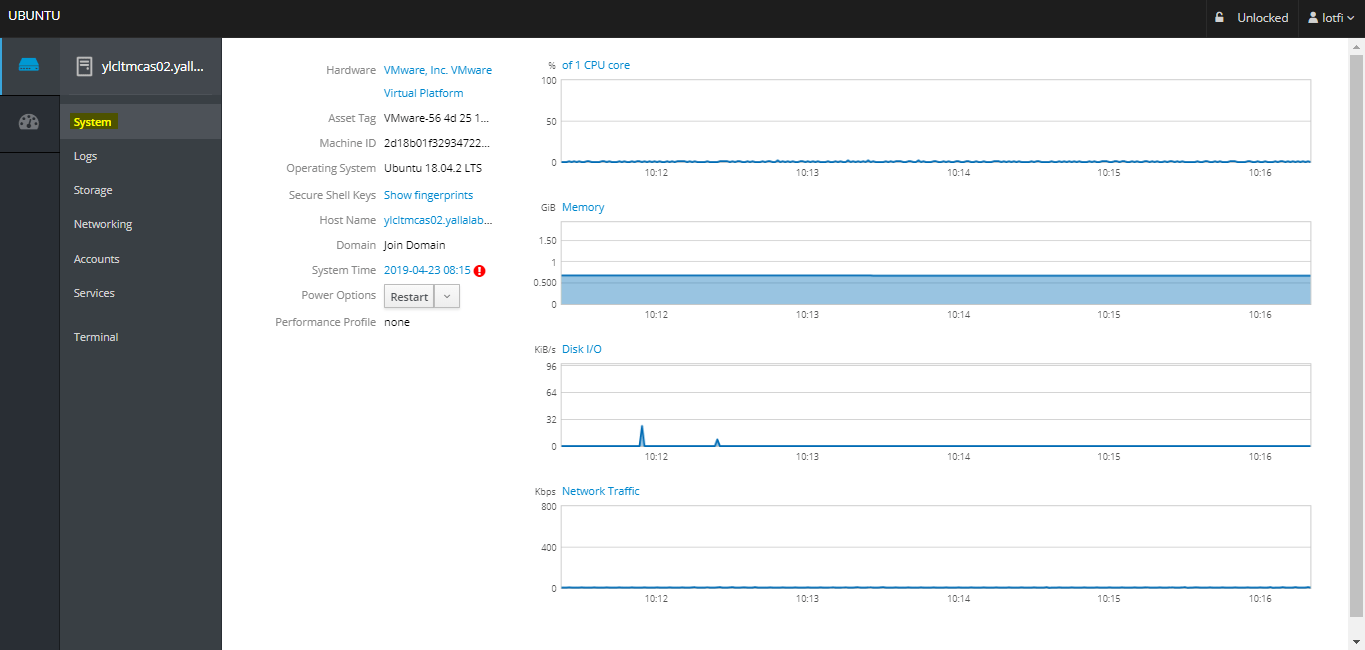
01- System Screen
– Once you have logged in, you will see the System Cockpit screen, shows information about the system that Cockpit is running on. This includes CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O, and network traffic, as well as hardware and operating system details.
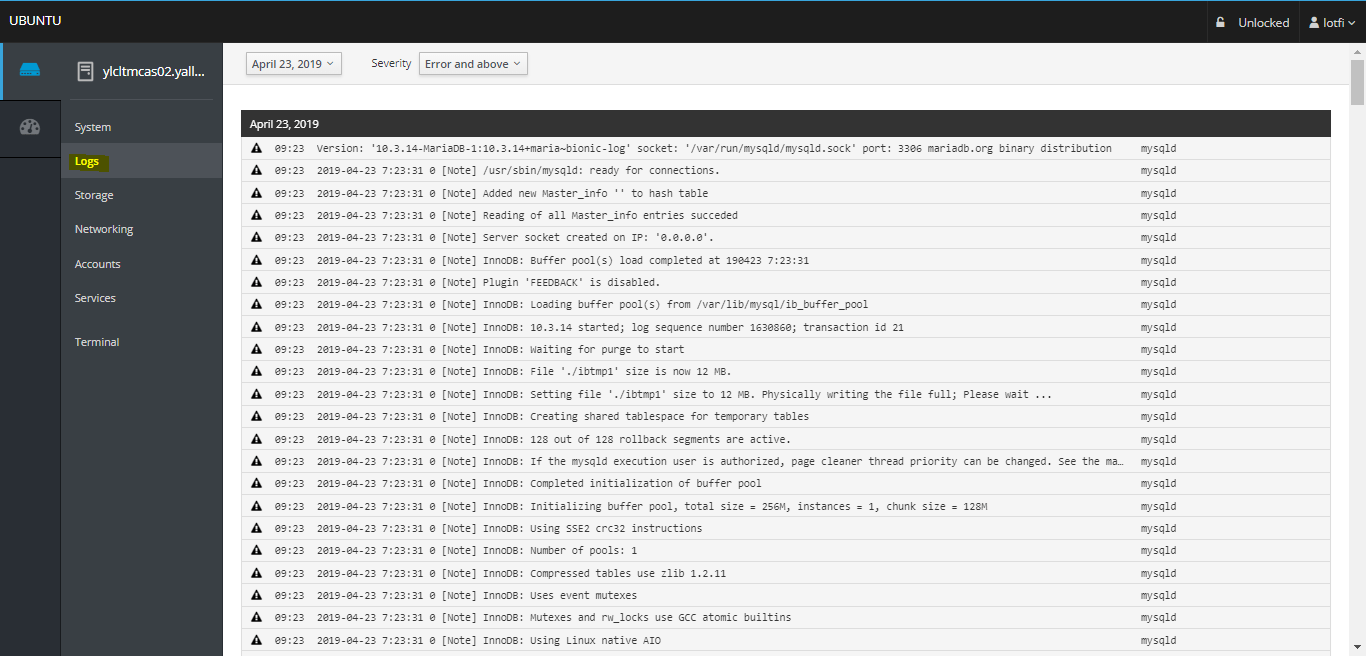
02- Logs Screen
– See messages produced by the systemd journal, including errors, warnings, and notices. The log is similar to the output of the journalctl command. The log displays newest entries first, with options to filter by type.
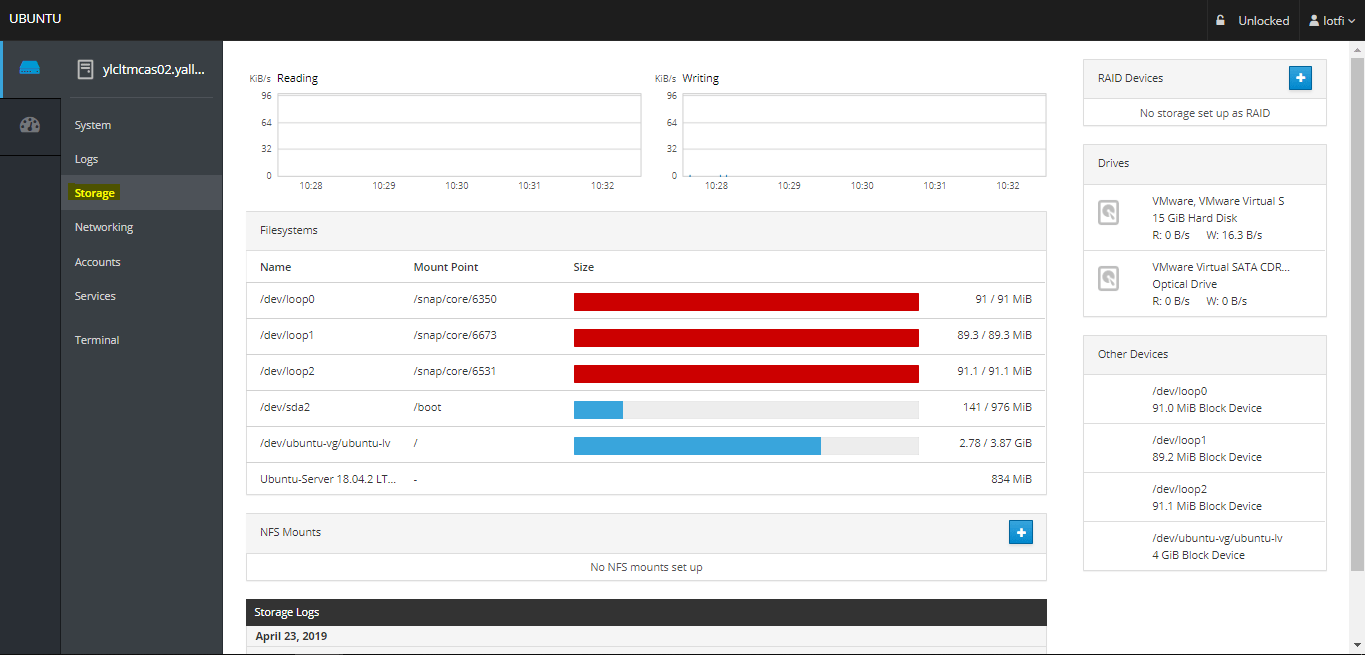
03- Storage Screen
– From the Storage menu section, you will see information concerning the hard drives and the Storage logs generated by your drives. In addition, you can add NFS Mount Points and setup RAID Devices:
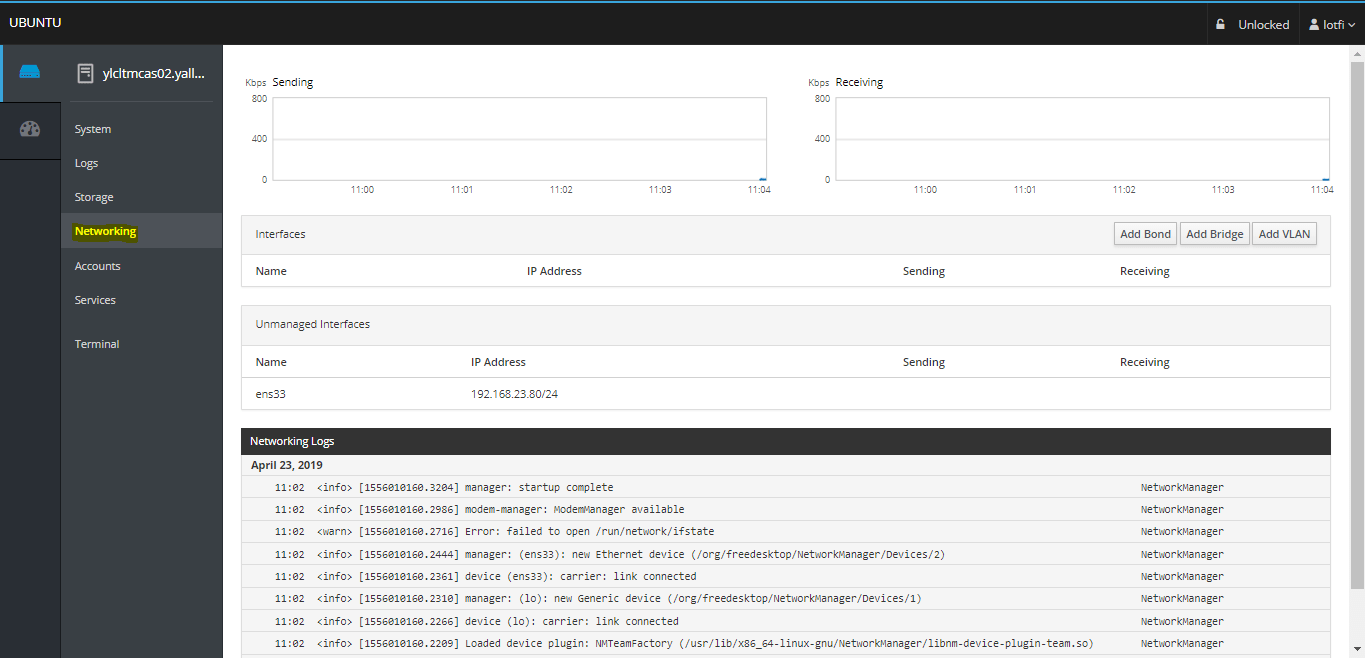
04- Networking Screen
– From the Networking menu section, you will see the information about networking interfaces and active graphs of sent and received data:
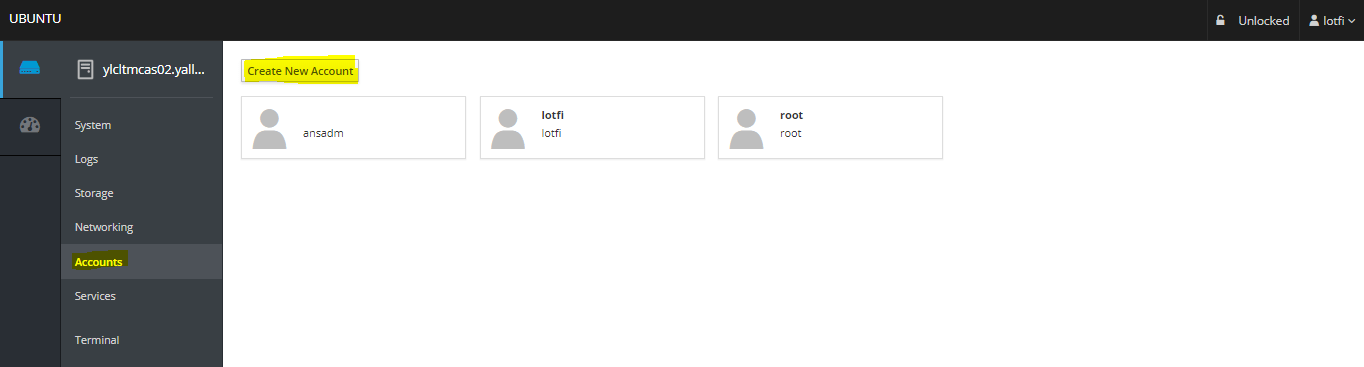
05- Accounts Screen
– From the Accounts menu section, you will see a list of the accounts on the system, you can even create a new accounts by clicking the Create New account button:
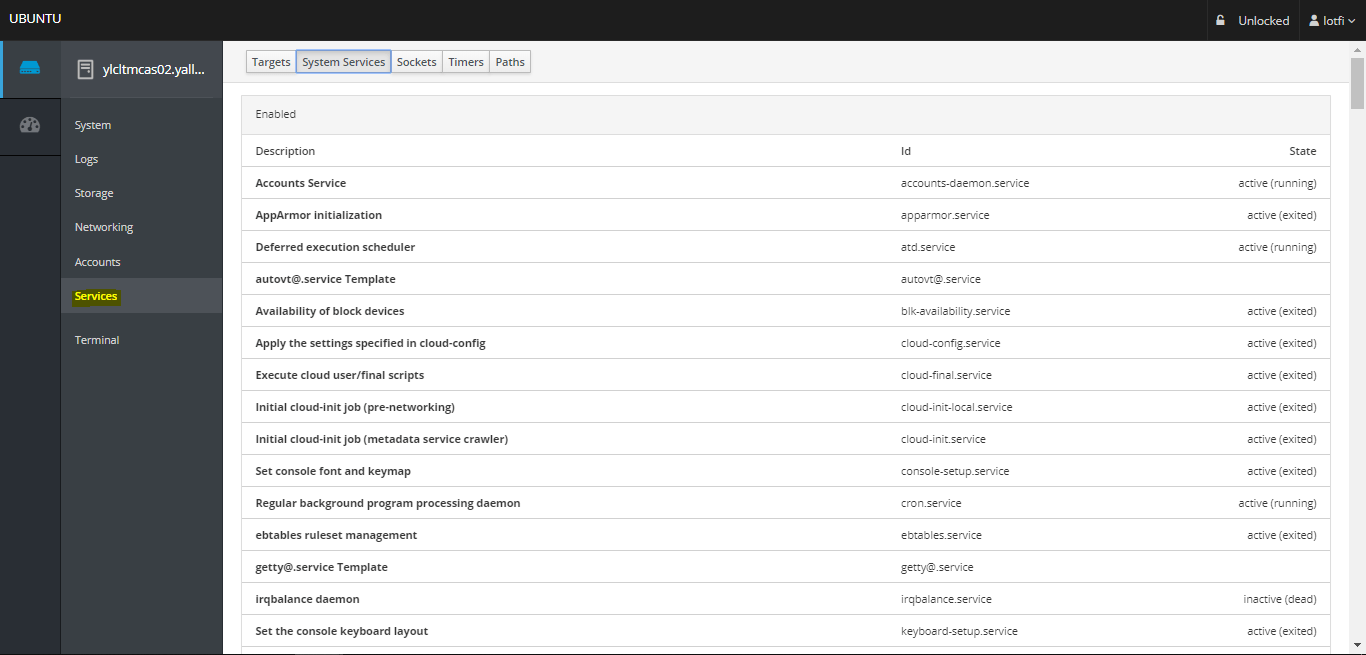
06- Services Screen
– The Services Section shows the systemd services running on the Cockpit server. You can see which are active/enabled or inactive. You can also see other systemd features: Targets, sockets, timers, and paths.
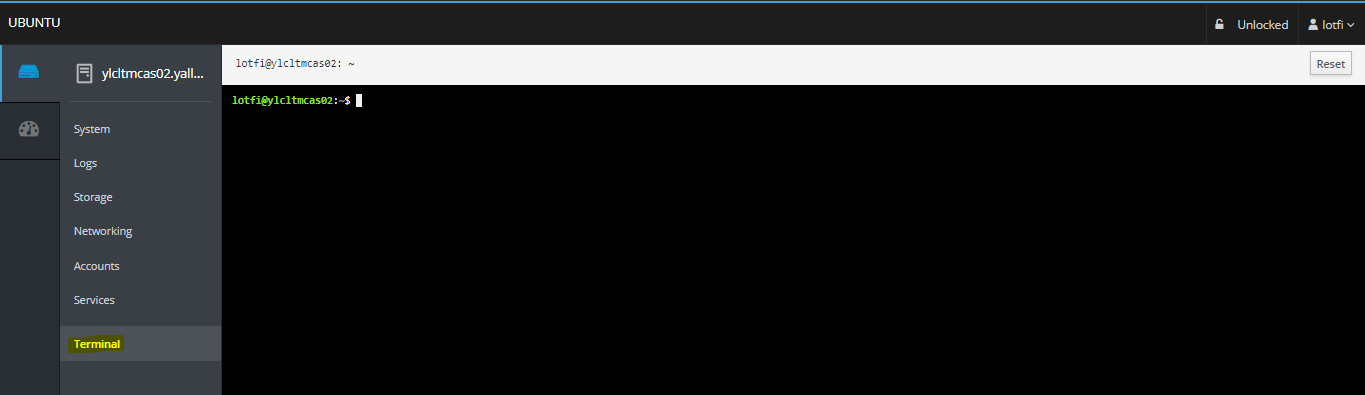
07- Embedded Terminal
– From the terminal session you can run commands from your signed-in user account:
Conclusion
You have successfully installed Cockpit on your Ubuntu 18.04 LTS / Ubuntu 16.04 LTS systems. For more information about Cockipt, check the Cockipt Documentation page.
See Also: